If you have ever written code in VBA, you have certainly come across the term Module. But what exactly is a module, and how does it differ from a class? In this tutorial from the free Iran VBA series, we will explore the different types of modules in VBA step by step and learn the differences between standard modules and class modules.
📑 Table of Contents
- What is a Module?
- Types of Modules in VBA
- Differences Between Standard Modules and Class Modules
- Frequently Asked Questions about VBA Modules
- What is a module in VBA?
- What is the difference between a standard module and a class module?
- How do I add a new module in VBA?
- Can public variables be used across all modules?
- What is the advantage of a standard module over a class module?
- What is the advantage of a class module over a standard module?
- Where and how should global variables be defined?
What is a Module?
According to Microsoft’s definition in the VBE Glossary, a module is a collection of declarations and procedures that together form an independent unit of code.
In English, a module means an independent piece or unit of a larger structure. In programming, it serves the same role: a part of the program that performs a specific task and can be developed separately and reused across different projects.
Types of Modules in VBA
In the VBA Editor (VBE), modules are organised into two main folders:
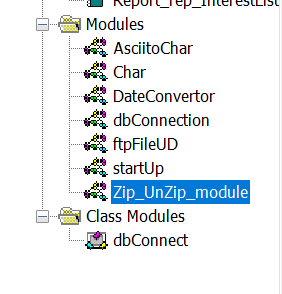
As shown in the image, there are two types of modules in VBA:
- Standard Modules – in the
Modulesfolder - Class Modules – in the
Class Modulesfolder
Standard Module
The standard module is what we most often work with. It contains procedures, functions, user-defined types (Type), and public declarations. The default access level in a standard module is public, meaning that its code is accessible from all parts of the project.
Uses of a Standard Module
Because a standard module has public access, it is suitable for storing code used across various parts of a project. Examples include helper functions, calculation routines, or global variables.
For example, if you have an application that needs to display the username across all forms, you can define a public variable in a standard module so it is accessible from everywhere.
In a standard module, the programming style is procedural. Code is written in procedures (Sub) and functions (Function), each performing a specific task.
Steps to Create a Standard Module
To add a standard module in Excel or Access, follow these steps:
-
Open the VBA Editor.
For more guidance, see the tutorial How to Open the VBA Editor.
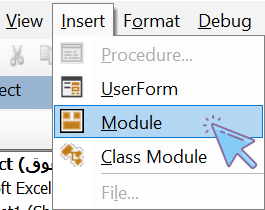
-
From the Insert menu, select Module.
This will create a new module in the
Modulesfolder (e.g., Module1). You can now write your code there and rename it if needed.
Class Module
A class module is a type of module used to define the details of a class. Each class contains properties and methods that define the behaviour of an object.
For example, you can create a class named clsEmployee with a property Name and a method ShowInfo. You can then create multiple independent instances (Objects) of it.
In future dedicated tutorials, we will fully cover Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in VBA.
Differences Between Standard Modules and Class Modules
| Feature | Standard Module | Class Module |
|---|---|---|
| Programming Type | Procedural | Object-Oriented |
| Nature | Library of public procedures and functions | Template for defining objects (Properties and Methods) |
| Instances | Single, not duplicable | Multiple independent objects can be created |
| Access Level | Public (throughout the project) | Dependent on created instances of the class |
Frequently Asked Questions about VBA Modules
What is a module in VBA?
A module in VBA is a place to store code, functions, and procedures. It helps make code more structured and reusable.
What is the difference between a standard module and a class module?
A standard module is used for writing general procedures and functions, whereas a class module is used to define objects with specific properties and methods.
How do I add a new module in VBA?
To add a new module, in the VBA Editor use the Insert → Module or Insert → Class Module menu. The selected type determines where the code will reside in the project.
Can public variables be used across all modules?
Yes, simply define the variable at the public level (using the Public statement) in a standard module to make it accessible across all modules and forms in the project.
What is the advantage of a standard module over a class module?
Standard modules are ideal for storing general-purpose functions and code that does not depend on a specific object. They are simpler and execute faster since no instance creation is required.
What is the advantage of a class module over a standard module?
A class module is useful when you want to define data and behaviour as an object. This allows better code organisation and the ability to create multiple independent instances of the same structure.
Where and how should global variables be defined?
Global variables should be defined in a standard module. At the top of the module, write:
Public VariableName As Type
This way, the variable will be accessible throughout the entire project.
Read More
Conditional and Logical Statements in VBA | Program Flow Control and Interactive Practice
Your First VBA Programme | Put Your Knowledge into Practice
Immediate Window | Understanding the VBA Immediate Window
VBA Built-in Functions | Complete List of Functions in Visual Basic
VBA Procedures | Definition, Types & Usage in Visual Basic
Constants in VBA | Types, Scope, and How to Use Them Effectively
Variable Scope in VBA | How to Access Variables across Different Parts of a Project



