VBA Code Editor, abbreviated as VBE (Visual Basic Editor), is a tool used for creating, editing, and maintaining VBA procedures and modules in Microsoft Office applications such as Excel and Access.
📑 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Section 1: Menu Bar
- Section 2: Toolbar
- Section 3: Project Explorer Window
- Section 4: Properties Window
- Section 5: Programming Window/Code Window/Module Window
- Section 6: Immediate Window
Introduction
The VBA Code Editor or VBE is a software environment where you can write, run, compile, and debug program code. In this section of Iran VBA’s free tutorials, we will examine different parts of this editor.
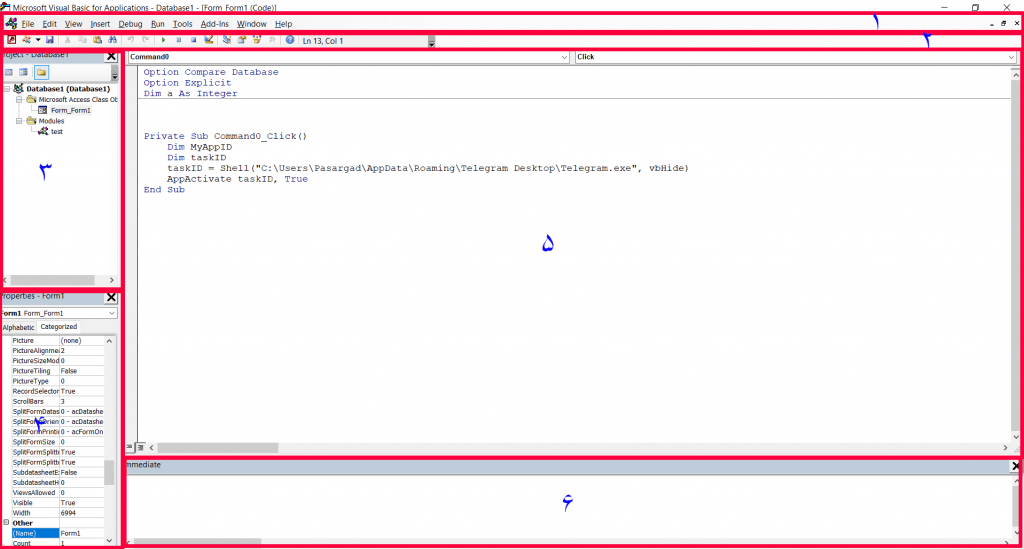
The default VBA Code Editor page can be divided into 6 main sections as shown in the figure, each of which we will explain in the following.
Section 1: Menu Bar
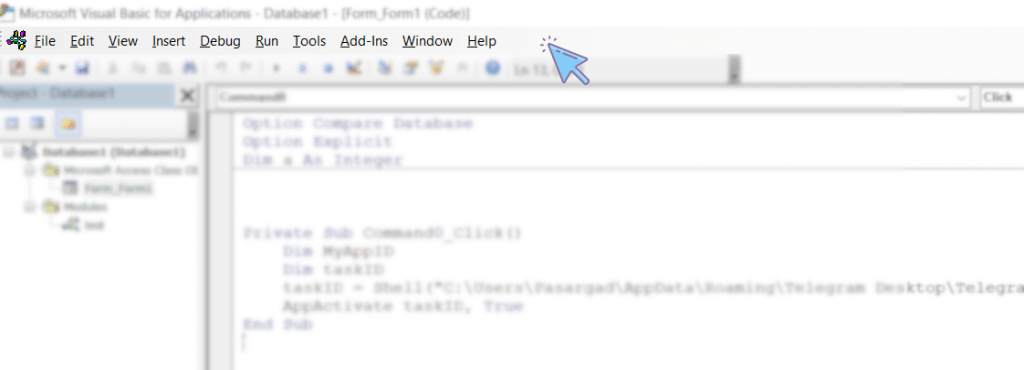
Like most Windows programs, VBE is also equipped with a menu bar. The menu bar contains various dropdown menus, each containing commands related to the menu title.
You may have noticed that some commands in the menus have shortcut keys displayed next to them. These shortcuts play an important role in increasing the speed of accessing frequently used commands.
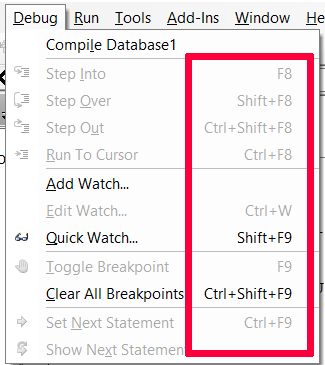
In the figure below, you can see the shortcut keys for commands in the Debug menu.
Section 2: Toolbar
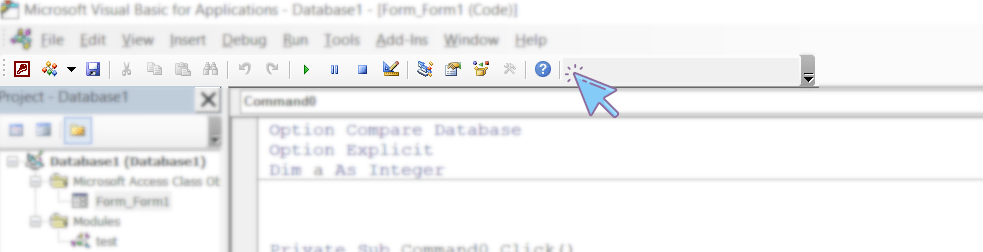
The toolbar, like the menu bar, is a familiar part of most computer programs. As shown in the figure, the toolbar consists of a series of tools and commands displayed to the user as icons.
The toolbar shown in the figure above is the standard VBA Code Editor toolbar, which is enabled by default in VBE. However, VBE also has three other toolbars:
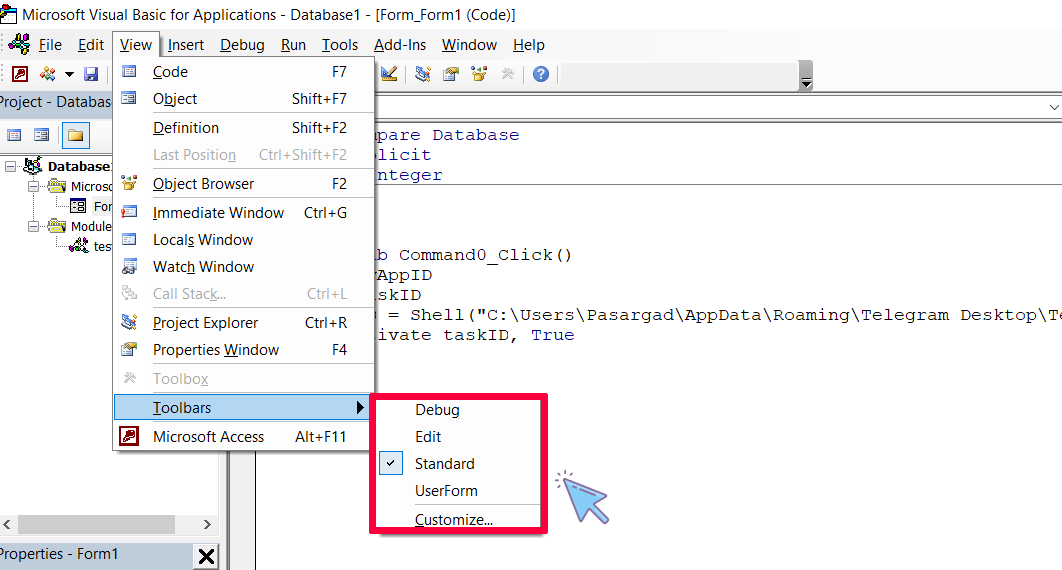
- Debug toolbar
- Edit toolbar
- UserForm toolbar
In addition to the above toolbars, VBE also provides users with the ability to customize the toolbar.
To change the toolbar or customize it, you can use the View menu and then select the Toolbars submenu.
Section 3: Project Explorer Window
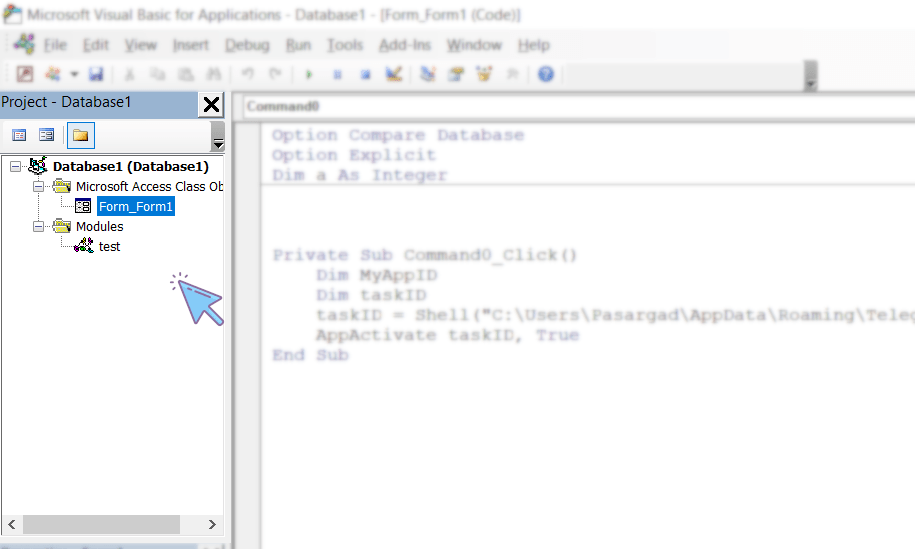
A Project in VBA is defined as a collection of modules. The Project Explorer window in VBE displays all modules available in a project.
VBE displays the project modules in this window as a tree diagram, categorized by module type.
If this window is inactive for you, you can activate it from the View menu by clicking on Project Explorer or pressing the Ctrl+R key combination. The different parts of the Project window are shown in the image below.
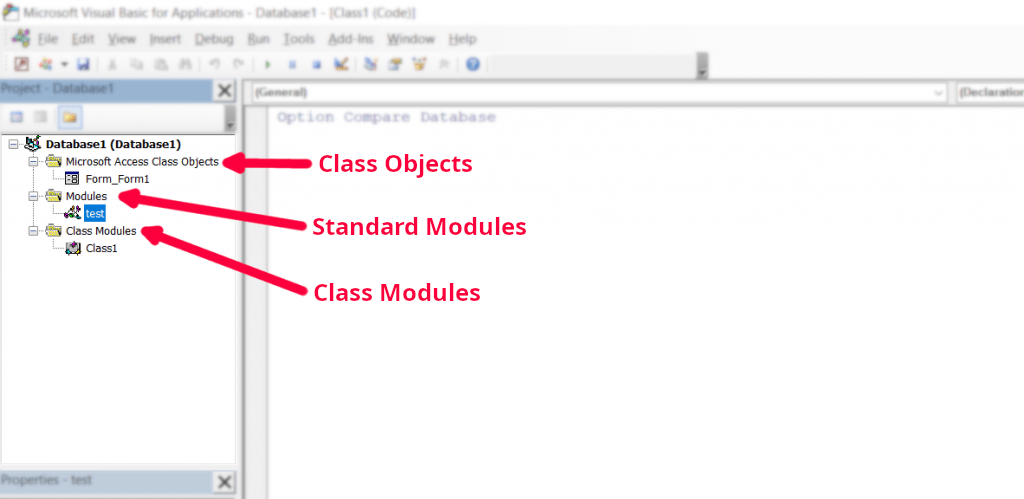
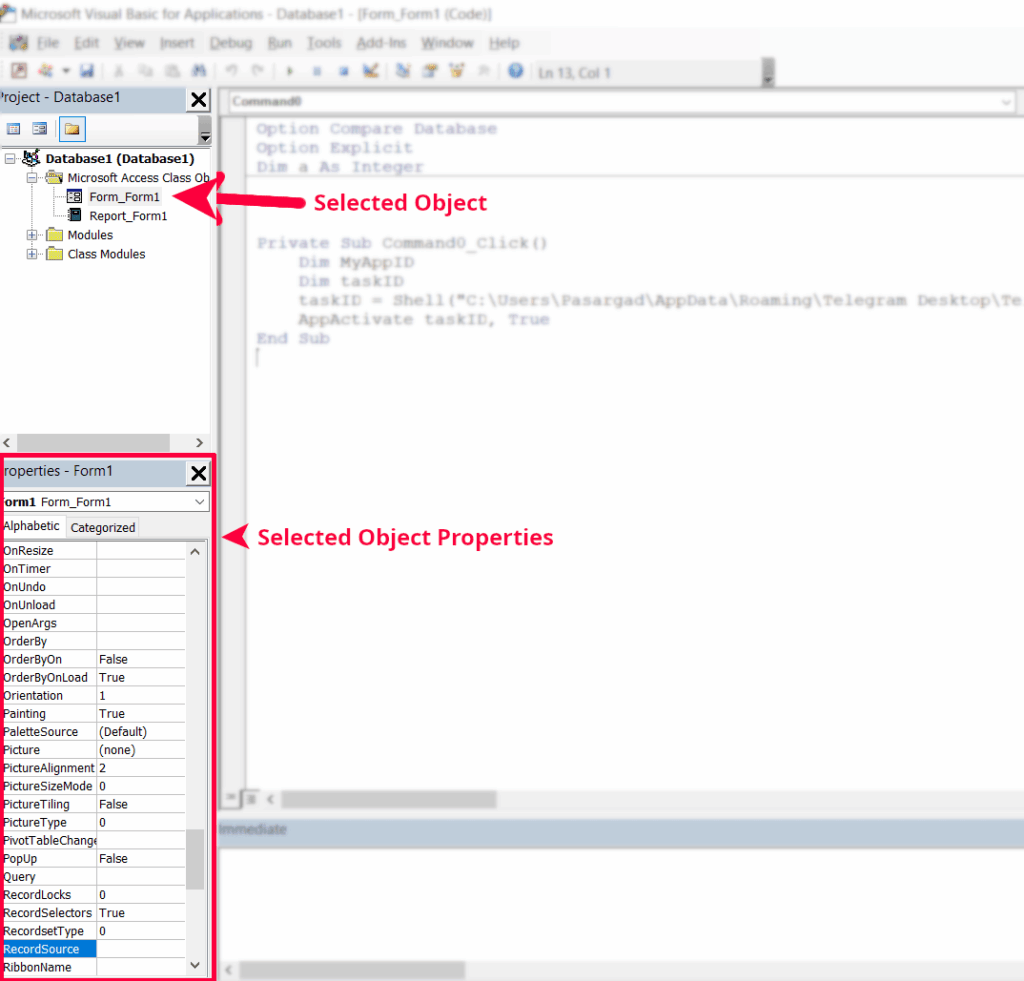
As shown in the image, class objects are objects designed by Microsoft and added by the user to the project.
For example, in the figure above, Form_Form1 is an Access form object saved by the user as Form1. Class objects in an Access file can be of form or report type.
The difference between standard modules and classes lies in the programming method used in these two modules. Programming in standard modules is procedural programming, while in class modules it is object-oriented programming.
It is noteworthy that class objects are essentially class modules that have been programmed and designed by Microsoft.
Section 4: Properties Window
The Properties window displays the properties of the class object that is in edit mode in the Project window. In this window, you can view the properties of a class or module.
For example, if you open a form in Design View in Access, the properties of the opened form will be displayed in this window.
If this window is not displayed in your code editor, you can display it again by pressing the F4 key or from the View menu.
Section 5: Programming Window/Code Window/Module Window
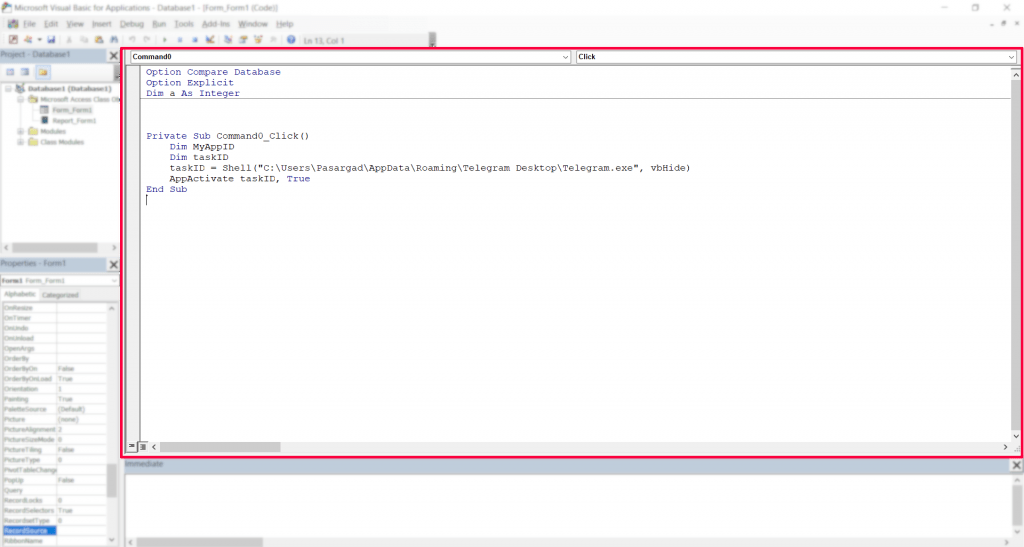
In this window, you can view or edit the codes stored in each module. This window functions similarly to a text editor.
To view the codes of any module, you can double-click on the desired module icon in the Project window.
Section 6: Immediate Window
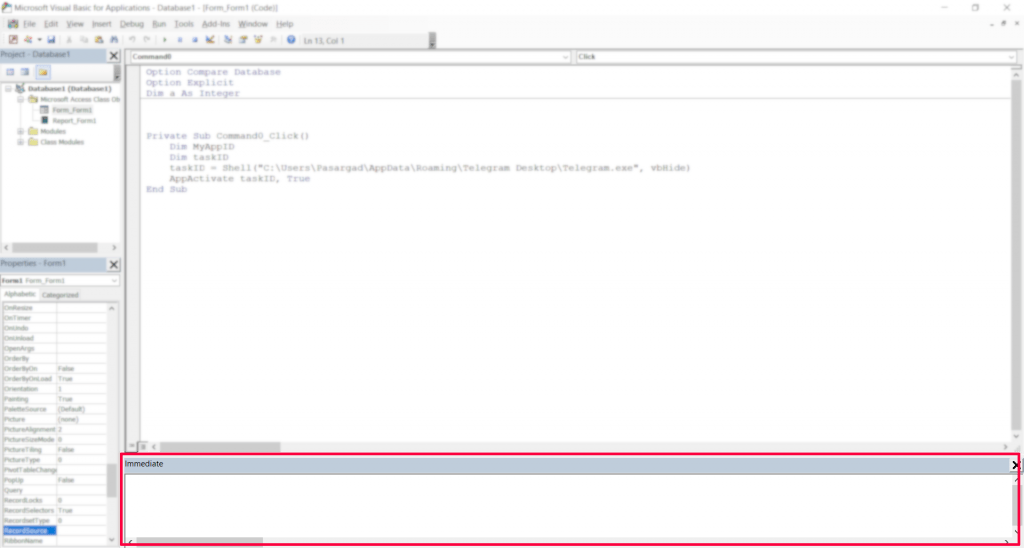
The main purpose of the Immediate Window is debugging and testing VBA codes. This window is the VBA programmer’s assistant in debugging codes.
While running program codes, you can view the contents of the Immediate Window by pressing the Ctrl+G key combination.
Read More
Conditional and Logical Statements in VBA | Program Flow Control and Interactive Practice
Your First VBA Programme | Put Your Knowledge into Practice
Immediate Window | Understanding the VBA Immediate Window
VBA Built-in Functions | Complete List of Functions in Visual Basic
VBA Procedures | Definition, Types & Usage in Visual Basic
Constants in VBA | Types, Scope, and How to Use Them Effectively
Variable Scope in VBA | How to Access Variables across Different Parts of a Project